A digital forensics specialist’s day starts with technology and investigation. Each workday is about discovering digital evidence and bridging the digital gaps using the digital forensics life cycle in cybersecurity. Starting from evidence recognition to reporting about it. Such specialists go deep into devices as well as networks to trace the particular cybercrime action. It works with preserving critical data and preparing court-ready research. Their role is necessary in today’s threatening world. Forensics specialists help organizations to investigate and understand how attacks happened. This makes the digital forensics lifecycle combat cybercrime and deliver justice.
Who Is A Digital Forensics Specialist?
A digital forensics specialist is one who is a trained cybersecurity investigator. They are responsible for collecting, preserving, and analyzing digital evidence. They abide by a strong investigative substructure, often called the digital forensics lifecycle, to make sure the evidence stays valid for legality. Their work guides cybercrime investigations, corporate security, and regulatory compliance.
Role and Responsibilities Of Digital Forensics
A digital forensics specialist plays an active role in revealing accurate digital proof and research. They abide by the digital forensics life cycle in cybersecurity to make sure the investigations are legal and technically sound. Below, we’ll take a look at the duties :
| Responsibility | Description |
| Evidence collection | Ensuring data is not altered and is secured in devices. |
| Forensic imaging | Creating the same copies of storage for further investigation. |
| Data Analysis | To recover deleted, hidden, or encrypted data. |
| Reporting | To create detailed yet understandable reports. |
| Consultation | Giving out advice for legal teams. |
These tasks are part of the digital forensics lifecycle which makes sure that each digital proof is performed professionally.
Importance Of Digital Forensics
In cybercrime, digital forensics is crucial. It helps investigators to reveal how a breach occurred, who was involved, and also what data was affected. It would be hard to get critical proof in court without the digital forensics lifecycle, if lost or dismissed. This profession gives clarity and accountability and strengthens the legal substructure in cybercrime incidents.
Start Of The Day: Morning Routine
The morning routine starts with case intake and prioritizing, then team briefings and planning by reviewing cases and what to prioritize.
Case Intake and Prioritization
A specialist starts by reviewing new cases and prioritizing those. Active threat cases or cases that have legal deadlines gain more focus. They take necessary actions by recognising the scope and the devices involved based on the digital forensics lifecycle in cybersecurity.
Team Briefings and Planning
After that, to allocate tasks and goals, they join team meetings. The plan includes setting several deadlines, choosing the best forensic tools, and confirming legal warrants.
Mid-morning: Evidence Collection & Imaging
This involves on-site evidence seizure and also forensic imaging on write blockers. These help with evidence collection and the imaging process.
On-site Evidence Seizure
Specialists go to crime scenes to seize devices while preserving the integrity of digital data. They abide by strong protocols to protect hardware without altering proof.
Forensic Imaging With Write Blockers
Write blockers are used when they create forensic images. Every bit copies of drives, as it helps with analyzing without risking the original data. This helps to preserve proof in the digital forensics lifecycle.
Noon: Deep Analysis Phase
This involves the use of file carving and keyword searches along with memory forensics and network analysis.
File Carving and Keyword Searches
While performing analysis, specialists bring out data that is either hidden or deleted. By performing a keyword you can find critical evidence faster. This is a crucial part of digital research.
Memory Forensics and Network Analysis
This involves analysing live memory or RAM. It also involves analysing network logs to track the attacker’s activities and arrange events step by step.
Late Afternoon: Reporting and Documentation
This includes reporting and documenting, and is the final stage. Requires the use of visualization. It provides quality assurance and court-ready report drafts.
Visualizations
Tech professionals create charts and timelines so that they can understand what they have found. These charts and timelines are really helpful for people who are interested in digital evidence technology to understand the current state of digital evidence.
Quality Assurance
When you are getting ready to finish your reports, make sure the work is checked carefully. This is so you can be certain that the job is accurate and complete. The work has to be checked multiple times to ensure that everything is correct and nothing is missing. This is an important step for reports, so take the time to do it properly.
Court-Ready Report Drafting
Finally, specialists assemble findings into structured, legal documents ready for use in cybercrime prosecutions.
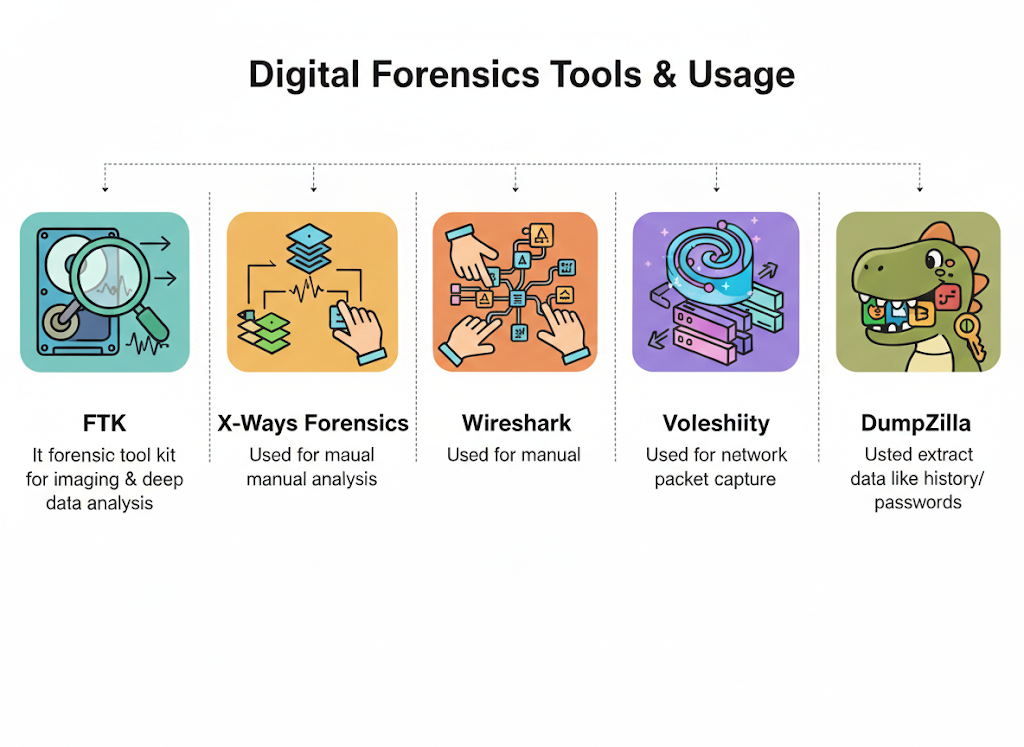
Tools and Technologies Used By A Digital Forensics Specialist
Digital forensics use much advanced tools for its digital forensics lifecycle. Below we discuss some tools so it’s easier to get an insight or a basic idea of the tools that are used during forensics investigation.
| Tools | Usage |
|---|---|
| FTK | It is a forensic tool kit used for imaging and deep data analysis. |
| X-Ways Forensics | Used for manual analysis. |
| Wireshark | Used for network packet capture. |
| Volatility | It is a RAM analysis tool. |
| DumpZilla | Used to extract browser data like history or passwords. |
Common Challenges Faced by Forensics Specialists
Digital forensics carries out confrontations such as encryption, which blocks access to the proof. Big amounts of data that take time to process. Dynamic tech that needs ongoing learning. Investigators also face legalities in their work, like cross-border data laws, and have to maintain custody chains. Such hurdles fill the data forensic lifestyle with complexities.
Career Path and Courses in Digital Forensics
At present, for India, entry pay varies, but specialists generally earn from INR 2.1 LPA to INR 18.5 LPA. Here, we discuss the various career paths related to Data forensics, and also get an insight into the salary as well.
| Career Path needs | About |
| Education | IT, Cybersecurity or Digital Forensics |
| Core skills | File system, networking, and forensic tools |
| Experience | Have experience in an internship with law enforcement |
| Job roles | Digital Forensic Expert, Cyber crime investigator, Forensic IT specialist and Malware Analyst. |
Some certifications suggested are DFE, CompTIAA+ and GCFE GCFA. Also, you can opt for courses related to Cybersecurity which are aligned to current industry trends.
All About Digital Forensics Lifestyle
Understanding the digital forensics lifecycle in cybersecurity is essential before pursuing a career in this high-impact field. From identifying critical evidence to delivering court-ready reports, digital forensics experts play a vital role in uncovering cybercrimes and ensuring justice is served. Their work demands precision, legal awareness, and technical expertise, while also building trust in investigations. With cybercrime evolving at a rapid pace, digital forensics stands out as a challenging yet highly rewarding career, offering strong growth, purpose, and long-term relevance in today’s security-driven world.
FAQs
What education is needed to become a Digital Forensics Specialist?
A career as a digital forensics specialist usually requires a degree in computer science, cybersecurity, or digital forensics, with certifications such as CHFI, GCFA, or another relevant certificate that is recognized by the profession. Students should receive exposure to networking, operating systems, the handling of digital evidence, legal standards and guidelines, as well as the complete digital forensics lifecycle and acquisition through reporting. Internships or lab work are very useful because hands-on experience in using tools builds skills you can draw upon for actual investigations.
What are the biggest daily challenges for forensics specialists?
Every day throws up new challenges that might involve getting to grips with encrypted data, wading through masses of information, or keeping pace with changing hardware or software. Specialists are forced into dealing with the stringent legal proscriptions, for example, the chain of custody and time constraints. Sensitive cases may require pinpoint reporting on a tight deadline. The tools change fast, so ongoing learning is a necessity in order to safely navigate through all stages of the digital forensics lifecycle.
What certifications are best for Digital Forensics in India?
Certifications that are best for digital Forensics in India are GIAC Certified Forensic Examiner or GCFE, GIAC Certified Forensic Analyst or GCFA, Certified Computer Examiner or CCE, certified forensic computer examiner or CFCE, Digital Forensics Essentials or DFE, EnCase Certified Examiner or EnCE.
What’s the average salary for Digital Forensics specialists in India?
At present, for India, entry pay varies, but specialists generally earn from INR 2.1 LPA to INR 18.5 LPA. Salary varies widely with your skills, the position of your job, and your expertise in tech. It even varies across different sectors.