Infection control protocols for nurses are standardized practices like hand hygiene, PPE usage, waste disposal, and isolation procedures that reduce infection spread in healthcare settings.
Infection control protocols for nurses are non-negotiable in modern healthcare. Nurses spend the most time with patients. That makes them the first line of defense against infections. Hospital-acquired infections affect millions globally every year. Many are preventable with strict protocol adherence. These protocols protect patients, staff, and communities. They also reduce legal risks for hospitals. For nurses, mastering infection control protocols is a core professional responsibility, not an optional skill.
In 2026, healthcare environments, infection control is no longer limited to ICUs. It applies everywhere. General wards. OPDs. Home healthcare. Telemedicine support roles. Every nurse must know these protocols thoroughly and apply them consistently.
What Are Infection Control Protocols For Nurses?
Infection control protocols for nurses are evidence-based practices designed to prevent the spread of infectious agents in healthcare settings. These protocols focus on breaking the chain of infection at every stage. They address how infections spread. They define how nurses should interact with patients. They specify hygiene, equipment handling, isolation, and waste management procedures. Protocols evolve with emerging diseases, antibiotic resistance, and global health trends. That is why continuous training is essential for nurses at all levels.
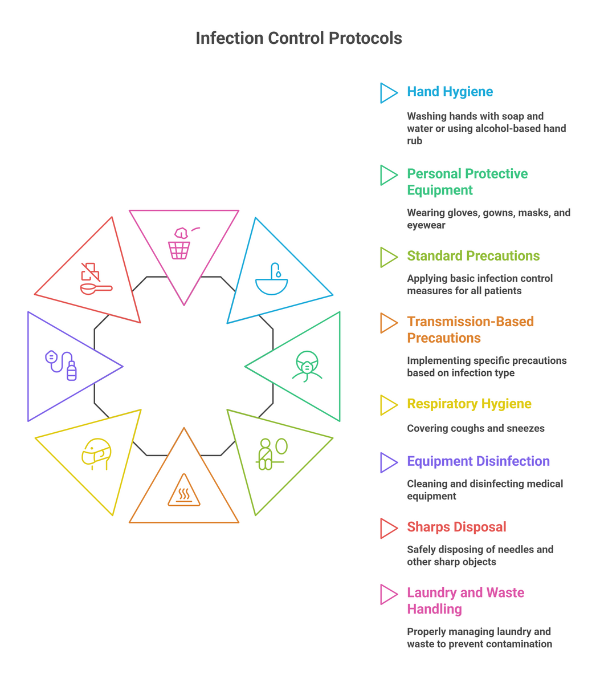
Standard Precautions: The Foundation of Infection Control
Standard precautions are the backbone of infection control protocols for nurses. They apply to every patient, regardless of diagnosis. These precautions assume that blood and body fluids may carry infection. Nurses must follow them at all times. Key principles include consistent hygiene practices, barrier protection, and safe handling of equipment. Ignoring standard precautions is one of the biggest contributors to infection spread in hospitals.
Hand Hygiene: The Most Critical Infection Control Protocol
Hand hygiene remains the most effective infection control protocol for nurses. It prevents cross-contamination between patients and surfaces. Nurses must clean their hands before and after patient contact. Before aseptic tasks. After exposure to body fluids. After touching the patient’s surroundings. Alcohol-based hand rubs are preferred when hands are not visibly soiled. Soap and water are mandatory when dealing with certain infections and after restroom use.
Compliance saves lives. Studies repeatedly show reduced infection rates with proper hand hygiene adherence.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Usage
Correct PPE usage is a core part of infection control protocols for nurses. PPE creates a barrier between healthcare workers and pathogens. Common PPE includes gloves, masks, gowns, face shields, and eye protection. Selection depends on exposure risk. Improper donning or doffing increases infection risk. Nurses must follow correct sequences to avoid contamination. PPE must be disposed of safely. Reuse is only permitted when protocols allow and sterilization standards are met.
Respiratory Hygiene and Cough Etiquette
Respiratory infections spread rapidly in healthcare settings. Infection control protocols for nurses emphasize respiratory hygiene. Patients with cough symptoms should be masked immediately. Nurses must maintain distance when possible. Ventilation should be optimized. Nurses should educate patients and visitors on cough etiquette. Covering the mouth. Using tissues. Proper disposal. Hand hygiene afterward. Simple actions significantly reduce airborne and droplet transmission.
Safe Injection and Sharps Handling
Injection safety is a critical infection control protocol for nurses. Unsafe injection practices lead to severe outbreaks. Nurses must use sterile needles and syringes for every injection. No reuse. No shortcuts. Sharps must be disposed of immediately in puncture-proof containers. Recapping needles is strictly discouraged. Needlestick injuries pose serious risks. Protocol compliance protects nurses from bloodborne infections.
Cleaning, Disinfection, and Sterilization
Environmental hygiene supports infection control protocols for nurses. Pathogens survive on surfaces longer than expected. Patient-care equipment must be cleaned between uses. High-touch surfaces require frequent disinfection. Sterilization protocols apply to surgical instruments and invasive devices. Nurses must understand the difference between cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization. Failure in environmental hygiene undermines all other infection control efforts.
Biomedical Waste Management
Proper waste management is a legal and ethical requirement. Infection control protocols for nurses include strict waste segregation. Waste must be categorized correctly. Sharps. Infectious waste. Pharmaceutical waste. General waste. Color-coded disposal systems reduce exposure risk. Incorrect disposal leads to infections and environmental hazards. Nurses play a key role in ensuring compliance at the point of generation.
Isolation Precautions for High-Risk Infections
Some infections require additional precautions. Infection control protocols for nurses classify isolation based on transmission mode. Contact precautions apply to multidrug-resistant organisms. Droplet precautions apply to respiratory infections. Airborne precautions apply to highly contagious diseases. Isolation rooms, PPE usage, and restricted movement are critical components. Nurses must monitor compliance among staff, patients, and visitors.
Role of Nurses in Preventing Hospital-Acquired Infections
Hospital-acquired infections increase patient morbidity and hospital costs. Nurses influence outcomes directly. By following infection control protocols for nurses, they reduce infection incidence. They also educate patients and families. Nurses act as infection control advocates. Their vigilance prevents outbreaks before they begin. Professional accountability matters. Consistent protocol adherence reflects nursing excellence.
Training and Compliance in Infection Control
Protocols are effective only when followed. Continuous training reinforces best practices. Simulation-based learning improves compliance. Audits and feedback ensure accountability. New nurses must be mentored. Experienced nurses must stay updated. Infection control protocols for nurses evolve. Learning must be ongoing.
Common Mistakes Nurses Must Avoid
Skipping hand hygiene due to workload is dangerous. Reusing PPE incorrectly increases risk. Improper waste segregation causes exposure. Ignoring isolation signage leads to outbreaks. Awareness reduces errors. Discipline prevents infections.
Why Infection Control Skills Boost Nursing Careers
Hospitals value nurses with strong infection control knowledge. It improves employability. Global healthcare systems prioritize patient safety. Infection control expertise is transferable across countries. Advanced roles require strong protocol understanding. Leadership opportunities follow competence. For nursing students, infection control mastery builds confidence early.
Build Industry-Ready Nursing Skills with edept
At edept’s NCLEX-RN training program, emphasis real-world infection control protocols for nurses. Practical training. Updated guidelines. Career-focused learning. Strengthen your clinical readiness. Protect patients. Advance your nursing career with edept and excel in Infection Control Protocols For Nurses.
Related Links:
FAQs
1. What are infection control protocols for nurses?
Infection control protocols for nurses are standardized practices that prevent the spread of infections in healthcare settings through hygiene, PPE, and safety measures.
2. Why are infection control protocols for nurses important?
Infection control protocols for nurses protect patients, healthcare workers, and communities by reducing hospital-acquired infections.
3. What is the most important infection control protocol for nurses?
Hand hygiene is the most critical infection control protocol for nurses and has the highest impact on infection prevention.
4. How do infection control protocols for nurses reduce hospital infections?
They break the chain of infection through proper hygiene, equipment handling, isolation, and waste management.
5. Where can nurses learn infection control protocols effectively?
Nurses can learn infection control protocols through structured training programs, clinical practice, and industry-aligned nursing courses like those offered by edept.